The online simulations of electrical quantity relationships on this page let you explore how the main electrical quantities in a circuit—voltage, current, and resistance—are related. Through different configurations, you’ll observe how current changes when voltage or resistance is modified and begin to recognize patterns that will help you better understand how electric circuits behave.
What does it mean for electrical quantities to be related
In an electric circuit, it’s not enough to understand each quantity in isolation. Voltage, current, and resistance don’t act independently, they’re interconnected. This means that changing one can affect the others. For example, if you increase the voltage of a power source, the current may also change. And if you adjust the resistance, the current might be affected as well.
Relationships between pairs of quantities
To understand how a circuit behaves, you need to look at how quantities relate to one another—not just at each one separately. This section explores the relationship between pairs of quantities. You’ll see that when one is held constant and another is changed, the third responds in a predictable way. These partial relationships will help you uncover a more general pattern behind circuit behavior.
Voltage and current
When you increase the voltage in a circuit, the current also increases. This happens because voltage acts like a “push” that drives the current more strongly. If the resistance in the circuit stays the same, that extra push results in more electric charge moving per second—in other words, a higher current. Put simply: higher voltage means higher current, as long as resistance remains constant. This direct relationship is one of the clearest patterns you can observe when adjusting a power source.
Current and resistance
In a circuit with constant voltage, increasing the resistance causes the current to decrease. It’s as if resistance adds more obstacles to the flow of current: the higher the resistance, the harder it is for charge to move. This means that higher resistance leads to lower current, as long as the voltage doesn’t change. This inverse relationship is another key pattern you’ll notice when analyzing how electrical quantities behave.
Voltage and resistance
In some cases, you may want to keep the current constant in a circuit. To do that, it’s not enough to fix just one quantity—voltage and resistance must be adjusted together. If you increase the resistance, you’ll also need to increase the voltage to maintain the same current. This shows that, while voltage and resistance aren’t directly related like in the previous cases, they are connected when trying to control circuit behavior.
Voltage, current, and resistance: Ohm’s Law
In the previous section, we looked at relationships between pairs of quantities. But the most interesting part comes when we relate all three. This relationship isn’t arbitrary—it follows a consistent pattern that appears in all circuits and is known as Ohm’s Law.
Ohm’s Law tells us that current is directly proportional to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance. In formula form:
I = V / R
In the simulations in this unit, you’ll see this relationship in action and confirm how it holds true in different scenarios.
Simulations of relationships between electrical quantities
- V-I
- I-R
- V-R
- V-I-R
Voltage and current
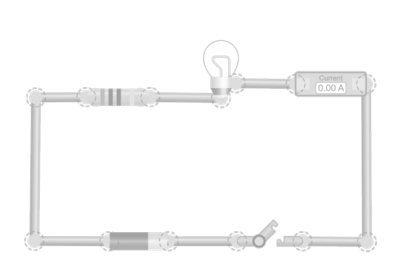
What happens to the current when you increase the voltage? In this simulation, you can adjust the voltage of the power source and observe how the current changes. Resistance remains constant so you can focus on the relationship between these two quantities.
Current and resistance
What happens to the current when you change the resistance? This circuit is the same as in the previous simulation, but this time you’ll try different resistance values while keeping the voltage constant. Watch how the current responds as the opposition to flow increases or decreases.
Voltage and resistance
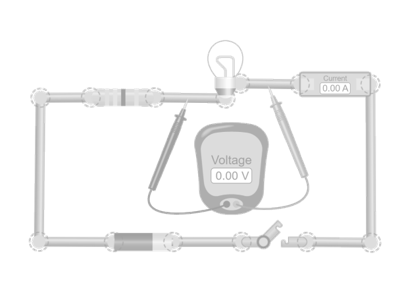
How can you keep the current constant? In this simulation, you can adjust both voltage and resistance. The challenge is to find combinations that keep the current unchanged. You’ll discover that to maintain the same current, voltage and resistance must be adjusted together.
General pattern. Ohm’s Law
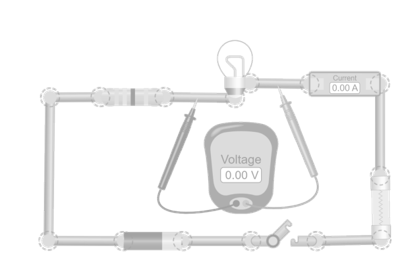
In this simulation, you’ll build a circuit with a battery, a resistor, a light bulb, and a fuse. You can change the voltage and resistance values and observe how the current changes. Pay attention to the bulb’s brightness, the fuse’s state, and the current readings. What happens when you increase the voltage? What if you change the resistance? Can you find different combinations that produce the same current? Experiment with the controls and see how the three electrical quantities are related. You’ll find that the same rule always applies: Ohm’s Law.
Giants of science
“If I have seen further, it is by standing on the shoulders of giants”
Isaac Newton

James Clerk Maxwell
–

Michael Faraday
–
Become a giant


Principles of Modeling, Simulations, and Control for Electric Energy Systems



Principles of Electric Circuits | 电路原理



Electrotechnique I



Electromagnetic Compatibility Essentials